How is the Modifier execution order defined from a business perspective ?
|
Order |
Modifier |
Reasoning |
|
1 |
HVAC Heat Pump |
The electrification modifier that has the most impact on the customer's load. It seems prudent to do this first before additional load is added to the customer Electrification modifiers are multiplicative i.e. appliance impact is multiplied against the customer’s interval data. This has the potential to create a mini-feedback loop as Modifier 2 impact will be multiplied against that of the customer’s interval data + Modifier 1 impact. |
|
2 |
Heat Pump Water Heater |
The electrification modifier that has the 2nd most impact on a customer's load. |
|
3 |
Electric Dryer |
The electrification modifier that has the 3rd most impact on a customer's load. |
|
4 |
Electric Range |
The electrification modifier that has the 4th most impact on a customer's load. |
|
5 |
Electric Vehicle |
EV is independent of the customer’s load as it creates a charging load that is added so it can go after the electrification modifiers but it’s important that it goes before solar and battery. |
|
6 |
Solar |
Solar should be sized to offset the customer’s consumption. Solar should be executed as the penultimate modifier to account for all potential changes to consumption.
|
|
7 |
Battery Storage |
The Battery modifier is intended to optimize the customer’s consumption and generation to reduce the bill and manage power outages. It should always be last to ensure it is sized for both the customer’s future consumption and generation load shape. |
How does it work from a technical perspective ?
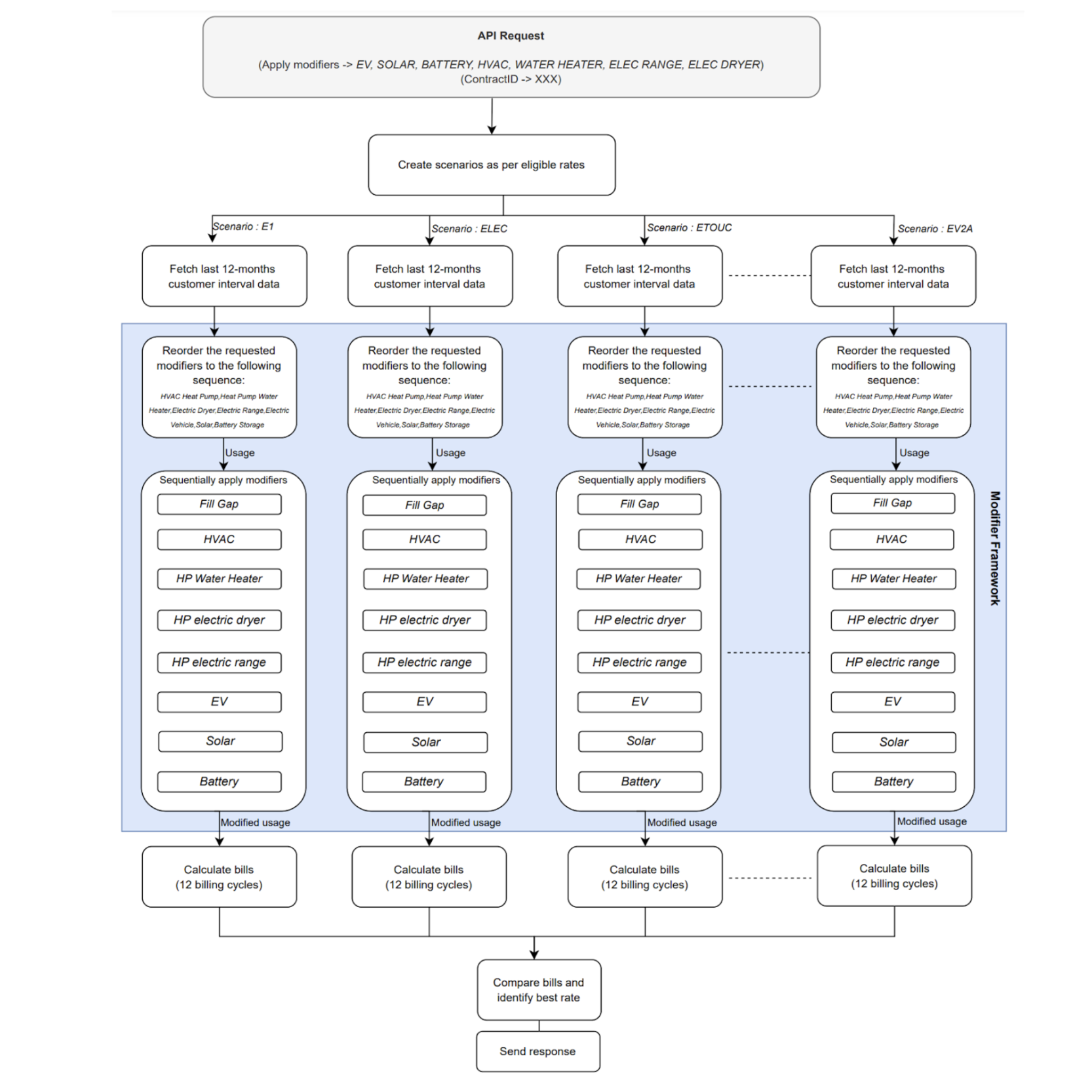
The diagram provided illustrates a high-level workflow for processing an API request (/compare-calculate) aimed at evaluating energy scenarios and identifying the optimal rate plans for a customer based on selected modifiers such as EV, Solar, HVAC, and others.
Customers can choose these modifiers from the explore UI, and the order of selection is not significant, as the system will reorder them according to business requirements.
The API request processing begins by retrieving 12 months of customer usage data, which is then passed through the modifier framework. Each modifier applies its specific algorithm to adjust the usage data before passing the modified results to the next modifier in the sequence.
Ultimately, the system generates bills using scenario-based rate models and compares them to determine the best rate for the request.
