Overview
The Heat Pump modifier is using the NREL’s ResStock to model the energy impact of a Heat Pump Climate Control system or Heat Pump Water Heater. The ResStock database of 550k virtual homes & “Upgrade” packages captures the energy impact of common electrification technologies.
Climate Control Heat Pump - Total Electricity Consumption
The percentage change of total energy for each interval is calculated for each analogous home, averaged, and applied the customer’s historical data
Climate Control Heat Pump - Electric Consumption Difference
The savings per interval is captured (negative values are energy savings).
Climate Control Heat Pump - User Input Parameters
The customer-facing UX features simple inputs that should be well-known to a homeowner. These parameters help identify the analogous homes within ResStock.
Heat Pump Water Heater - Total Electricity Consumption
The percentage change of total energy for each interval is calculated for each analogous home, averaged, and applied the customer’s historical data.
Heat Pump Water Heater - Electric Consumption Difference
The savings per interval is captured (negative values are energy savings).
Heat Pump Detailed Compute Structure
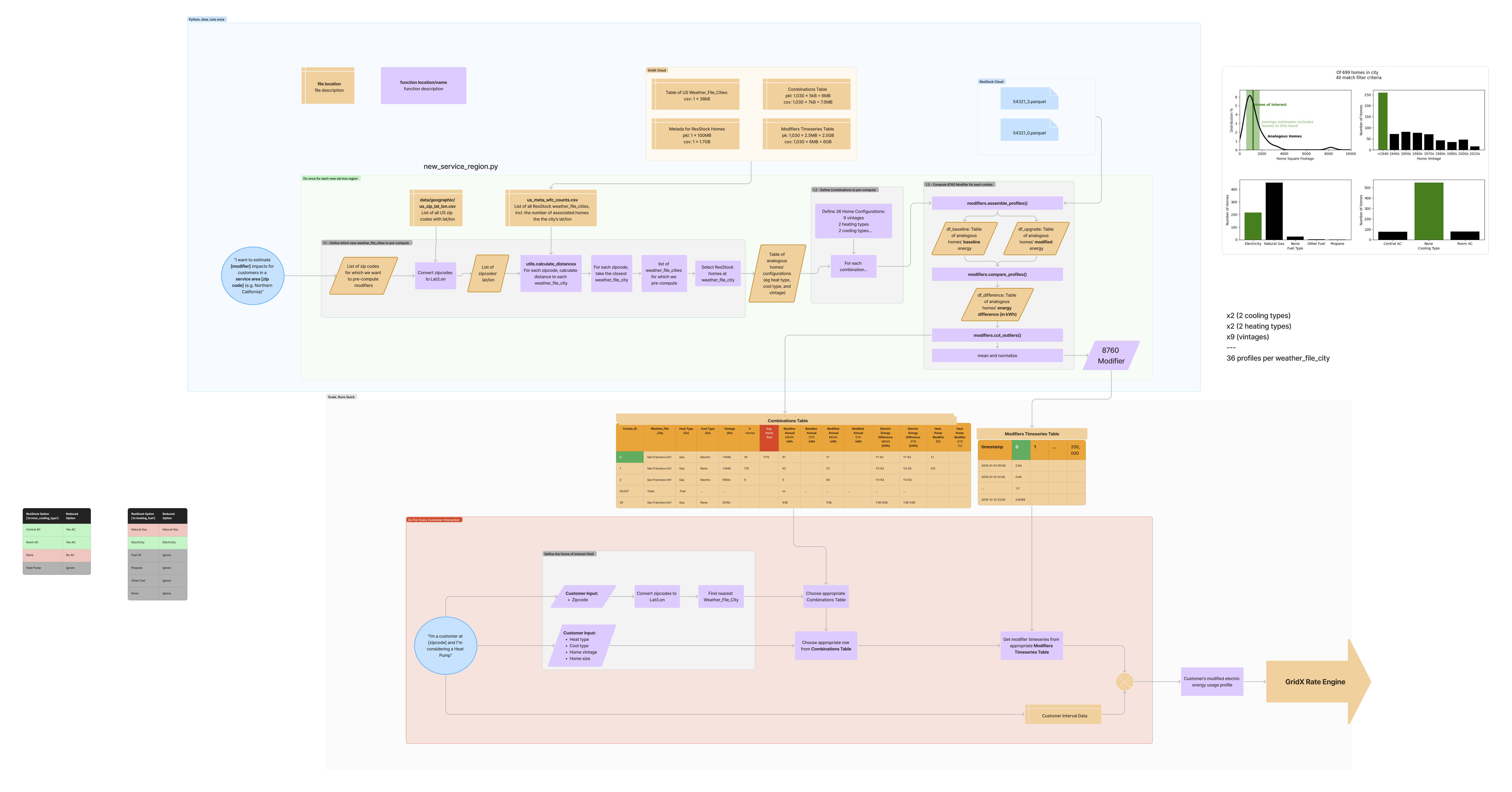
Gas Modifier – Methodology & Integration
As part of the Heat Pump modifier, the Gas Modifier also leverages NREL’s ResStock data to estimate the impact of a heat pump-based retrofit on natural gas usage. We identify a pool of “analogous” ResStock homes (based on climate zone, building vintage, and existing heating/cooling types) and compare their hourly gas usage before and after the heat pump upgrade.
For each analogous home, we compute the difference in gas consumption (post-upgrade minus pre-upgrade) at each hour of the year. We then filter out outliers using a z-score threshold, average the remaining differences across all homes, and apply that average hourly difference to the customer’s actual gas profile. This yields an additive Gas Modifier: negative values represent savings (reduced gas usage), while positive values (if any) capture scenarios where the upgrade might lead to increased gas usage under certain conditions.
In parallel with the reduction in gas usage, there is also an increase in electric usage from the newly installed heat pump—similar to how electrification of other gas-fueled appliances (ranges, dryers, etc.) reduces one fuel while increasing another. While the Gas Modifier focuses on the natural gas portion, the overall Heat Pump modifier pipeline consistently models both effects.
